Comprehensive Guide to Government-Supported Electrician Training in Canada
The electrical industry in Canada offers stable, well-paying careers with strong demand for skilled electricians. With government-supported training programs, individuals can gain hands-on experience, certification, and job placement assistance without accumulating significant student debt. This guide covers electrician training programs, certifications, career progression, and salary expectations in Canada.

🏛️ Government-Supported Training Programs
Canada provides various federal and provincial programs to help individuals enter the electrical trade. These programs include:
Red Seal Electrician Apprenticeship Program 🔴 – A nationally recognized certification allowing electricians to work across provinces.
Provincial Skilled Trades Programs 🏗️ – Each province offers funding and training for electricians through apprenticeship boards.
Workforce Development Grants 💰 – Government subsidies to cover tuition, tools, and licensing fees for eligible trainees.
Employment Insurance (EI) Training Support 📚 – Unemployed workers may qualify for financial assistance while completing electrician training.
Participants in these programs can access:
Tuition-Reimbursement or Low-Cost Training 🎓 – Financial aid covers classroom instruction and on-the-job training.
Paid Apprenticeships 💰 – Earn while learning through employer-sponsored apprenticeship programs.
Job Placement Assistance 🔧 – Government and trade associations connect trainees with licensed electricians and contractors.
🔧 Basic Electrician Training
⏳ Fast-Track Training Duration
Unlike traditional 🎓 four-year degree programs, electrician training programs are designed for ⚡ quick employment,📜 Certificate Programs: 3-6 weeks ⏳
Many government-supported electrician training programs are designed for quick job placement, with courses lasting only 3-6 weeks. These accelerated programs allow trainees to gain essential skills and enter the workforce faster while continuing their education through apprenticeships.
✅ Safety & Compliance Training
Electricians must follow Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) standards to ensure safe work environments. Training includes:
Electrical Safety Protocols ⚡ – Prevent electrical hazards, shock, and fire risks.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Use 🦺 – Learn proper use of gloves, helmets, and insulating tools.
Workplace Safety Training 🏗️ – Comply with Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS) regulations.
✅ Electrical Fundamentals
Electrician training includes classroom instruction and hands-on experience in:
Basic Electrical Theory 🔌 – Understanding circuits, voltage, and resistance.
Wiring & Circuitry 🏠 – Installation of residential, commercial, and industrial wiring systems.
Blueprint Reading 📜 – Learning to interpret electrical plans and schematics.
🎓 Certification & Licensing Requirements
The main requirements for electricians to obtain provincial certification include:
Electrical Apprentice License 🎓 – Required to work under a licensed electrician.
Journeyman Electrician Certification 🏅 – Granted after completing apprenticeship and passing exams.
Red Seal Endorsement (RSE) 🔴 – National certification allowing work across provinces.
Specialty Certifications 🔧 – Additional training for high-voltage, automation, or renewable energy systems.
📈 Career Progression & Salary Expectations
Most electricians start as apprentices and gradually advance to higher-paying roles. Career growth includes:
| Experience Level | Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Apprentice (0-4 years) | $40,000 - $60,000 |
| Journeyman Electrician (4-10 years) | $65,000 - $90,000 |
| Master Electrician (10+ years) | $100,000 - $140,000+ |
Union electricians typically earn higher wages and benefits.
Specialized electricians (e.g., industrial or high-voltage technicians) can earn over $140,000 annually.
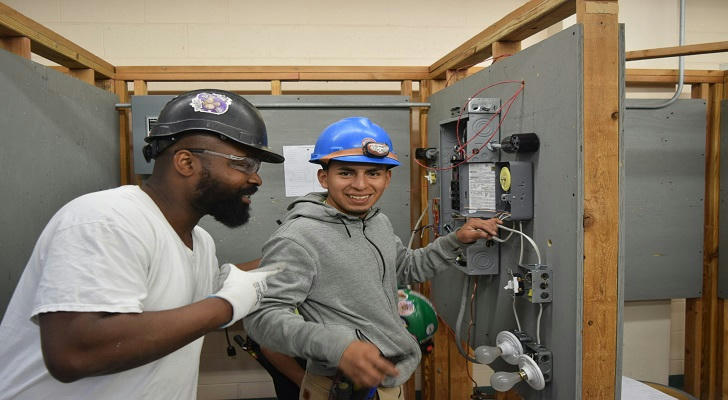

🌟 Benefits of Becoming an Electrician in Canada
✅ Job Security & High Demand
Growing Industry 📈 – The demand for electricians is expected to rise 8% over the next decade.
Essential Trade 🏗️ – Electricians are needed in construction, manufacturing, and renewable energy sectors.
Government Infrastructure Projects 🚧 – Increased funding for power grids and green energy boosts job opportunities.
✅ Competitive Salaries & Benefits
Paid Overtime & Bonuses 💰 – Many electricians earn extra income through overtime and shift differentials.
Pension & Retirement Plans 🏦 – Employer-contributed RRSPs and union pension funds.
Medical & Dental Coverage 🏥 – Many employers provide full healthcare benefits.
✅ Fast-Track Career Entry
No University Degree Required 🎓 – Training through apprenticeships instead of costly university programs.
Earn While You Learn 💵 – Apprentices work and earn wages while training.
Flexible Work Opportunities 🏠 – Many electricians become self-employed or start their own businesses.

⚡ Start Your Electrician Career in Canada Today!
Becoming a licensed electrician offers high wages, job stability, and career growth with government-supported training programs. Whether you're interested in residential, commercial, or industrial electrical work, there are apprenticeships and certification programs to help you succeed. 🚀
👉 Take the first step toward a rewarding trade career—apply today!
For more information, visit Apprenticeship Training in Canada